
Parathyroidectomy is the surgical removal of one or more parathyroid glands.
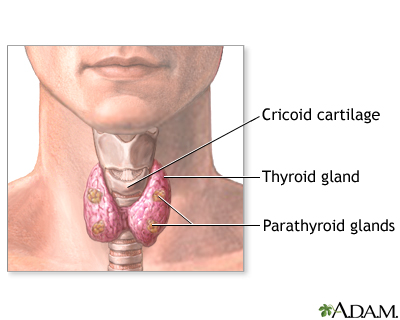
The parathyroid glands are four rice-sized glands located on back of the thyroid gland in the neck. The parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH), which controls the levels of calcium in the body.

In patients with hyperparathyroidism, one or more parathyroid glands become enlarged and oversecrete parathyroid hormone, causing levels of calcium to rise in the blood.
Surgery to remove the enlarged gland (or glands) is the only definitive treatment for the disorder and cures it in 95 percent of cases.
With the use of accurate preoperative imaging studies and intraoperative parathyroid hormone measurement, minimally invasive parathyroidectomy via a 2-3 centimeter incision is possible in the majority of cases.
Your health care provider may recommend this surgery if one or more of your parathyroid glands is producing too much parathyroid hormone. This condition is called hyperparathyroidism. It is often caused by a small non-cancerous (benign) tumor called an adenoma.
Your surgeon will consider many factors when deciding whether to do surgery and what type of surgery would be best for you. Some of these factors are:
Symptoms can be vague in the early stages of hypercalcemia. As the condition progresses, you may have:
People with no symptoms may only need monitoring. Mild cases can be managed medically. However, if hypercalcemia is due to primary hyperparathyroidism, only surgery that removes the affected parathyroid gland(s) will provide a cure.
The most serious consequences of hypercalcemia are:
This may due to the buildup of calcium in the arteries and heart valves.
Risks for anesthesia and surgery in general are:
Risks for parathyroidectomy are:
Parathyroid glands are very small. You may need to have tests that show exactly where your glands are. This will help your surgeon find your parathyroid glands during surgery. Two of the tests you may have are a CT scan and an ultrasound.
Before surgery, an anesthesiologist will review your medical history with you and decide what type of anesthesia to use. The anesthesiologist is the doctor who will give you the medicine that allows you to sleep and be pain free during surgery and who monitors you during surgery.
Tell your surgeon:
During the week before your surgery:
On the day of your surgery:
Often, people can go home the same day they have surgery. You can start your everyday activities in a few days. It will take about 1 to 3 weeks for you to fully heal.
The surgery area must be kept clean and dry. You may need to drink liquids and eat soft foods for a day.
Call your surgeon if you have any numbness or tingling around your mouth in the 24 to 48 hours after surgery. This is caused by low calcium. Follow instructions about how to take your calcium supplements.
After this procedure, you should have routine blood tests to check your calcium level.
People usually recover soon after this surgery. Recovery may be fastest when less invasive techniques are used.
Sometimes, another surgery is needed to remove more of the parathyroid glands.
Removal of parathyroid gland; Parathyroidectomy; Hyperparathyroidism – parathyroidectomy; PTH – parathyroidectomy
Dear All
In view of the COVID 19 attack, we at Suman Clinic want to initiate online consults which will benefit our patient’s Consultants available for online consultation except for Sundays.
Steps to follow